Indian Railways in Postal Stamps
by Vikas Singh
A collection of images of stamps pertaining to railways in India, from the author's collection, along with notes and technical details.
Also see Vikas's article on IR-related First Day Covers, article on IR-related coins and cards, and the album of railway-related postage stamps in the picture gallery. Apart from these IRFCA resources, there are some collections of IR-related philatelic material accessible on the Internet. One example is Sandeep Chaurasia's collection.
Mail Train

This 4-anna stamp released in 1937 depicts a portrait of King George VI and a 4-6-2 steam loco of East Indian Railways along with mail cars.
Date of issue: 23.8.1937
Denomination: 4 annas
Railway Centenary

On April 16, 1853 a train with 14 railway carriages, 3 locomotives Sindh, Sultan and Sahib, and 400 guests left Bombay at 15:35 hours. This was India's first rail run. The train left Bori Bunder for Thane with a 21-gun salute and the Governor's band to see it off. The journey took an hour and fifteen minutes. Vulcan Foundry, England manufactured the locomotives used on this run. A total of eight engines, GIP Nos 1-8 and bearing makers numbers 324-331, were ordered from the foundry in 1852 and the locomotives were of the type 2-4-0. These were the earliest known locomotives in service in India then. The earliest steam locomotive still in service has been certified by Guinness as the Fairy Queen. This is a 2-2-2 type locomotive manufactured by Kitson, Thompson and Hewitson, UK for the East Indian Railways (EIR). Kitson and Co supplied these locomotives (2 in number) in 1855. These were numbered 21 and 22 and later renamed EIR 91 and 92. They acquired the names Express and Fairy Queen respectively in 1895.
After the first railway line had been opened, railway development in India followed the course of least resistance and maximum profit. The increase in mileage was phenomenal:
| Year | Mileage open |
|---|---|
| 1853 | 20 |
| 1860 | 838 |
| 1870 | 4791 |
| 1880 | 8996 |
| 1890 | 16404 |
| 1900 | 24752 |
| 1910 | 32099 |
| 1920 | 36735 |
| 1930 | 41724 |
| 1937 | 43128 |
From the beginning up to 1869, the construction and working of railways was left entirely to companies with some form of guarantee. From 1870 to 1880 all new lines ware constructed by the direct agency of the state and with state funds. From 1880 up to 1907 the operations of both the state and aided companies went on side by side. From 1907 onwards all major lines were purchased by the government and leased to private companies for operation.
The 2-anna stamp depicts 2-2-2T 'Express' of 1853 and WP-1 of 1953.
Date of issue: 16.4.1953
Denomination: 2 annas
Centenary of Postal Transportation

On October 1, 1954, India completed 100 Years of the issue of its First Postage Stamp, which also coincided with the placing of the Post Offices under the centralized control of a Director General. India has the unique honor of being the first country in Asia to issue postage stamps. To celebrate the historic occasion of the Centenary of India Postage Stamps on 1st October 1954, the Department issued four commemorative stamps, in denominations of 1 anna, 2 annas, 4 annas and 14 annas depicting the different modes of carrying mails during these 100 Years.
The 4-anna stamp depicts a 4-6-2 class WP-1 steam loco and mail cars.
Date of Issue: 1.10.1954
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works

Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) a premier production unit of Indian Railways is situated in Chittaranjan, 250 Km. from the nearest Metropolitan city of Calcutta in the state of West Bengal. Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) has been named after the great freedom fighter, leader and statesmen Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das. The production activity started on 26th January 1950 the day when India became Republic. The initial product of Chittaranjan Locomotive Works was Steam Locomotive. In the period 1950-1972 Chittaranjan Locomotive Works turned out a total number of 2351 Steam Locomotives. In 1971-72 the last Steam locomotive rolled out. In the period 1967-93, Chittaranjan Locomotive Works has also turned out 842 Diesel Hydraulic Locomotive. The production of Diesel Hydraulic Locomotive was discontinued in 1993-94. The production of Elect. Locomotive was started in 1961-62. Chittaranjan Locomotive Works has always kept space with time and technology up gradation in a continuous manner. With the roll out of first CLW built WAG-9 3-phase elect. Locomotive 'NAVYUG' on 14.11.1998, India joined a select club of 5 countries who can manufacture elect. locomotive with 3-phase technology
The 8-anna stamp depicts 2-8-2 class WG steam loco built at CLW
Date of issue: 26.01.1955
Denomination: 8 annas
Chittaranjan Das

Among the personages who shaped the destiny of the Indian struggle for freedom, Chittaranjan Das ranks as one of the most outstanding and prominent patriots who sacrificed his all for the country's cause. Born on 5th November 1870, C. R. Das had his early education in the London Missionary Society Institution, Bhowanipur, and graduated in 1890 from the Presidency College, Calcutta. He then proceeded to England where he joined the middle temple and was called to the Bar in 1892. He returned to India in 1893 and enrolled himself at the Bar of the Calcutta High Court. During his early years as a lawyer intimately associated as a budding poet with Rabindranath Tagore. After a series of sensational criminal cases in which he appeared to use his vast knowledge of British Law for the defense of patriots and the advancement of the cause of India's freedom, the most famous of which was the case in which he defended Sri Aurobindo Ghose accused in the Alipore Bomb Conspiracy case, and his success in a number of civil cases, particularly the Dumroun adoption case, his reputation as a brilliant lawyer was established. He gave up his lucrative practice, which was fetching him a princely income while at the height of his profession in order to through his weight fully into the freedom struggle. Although revolutionary in his ideas, he was apposed to violence and was a staunch votary of constitutional methods. A founder of the Swaraj Party within the freedom movement, he advocated fighting the British Raj from within the council chambers. True to his own statement 'If I live, I live for Swaraj, If I die, I die for swaraj', Chittaranjan Das thought, dreamt, talked and worked for the freedom of India and nothing else till the very day of his untimely death on 16th June, 1925. A brilliant barrister, poet, journalist and philanthropist, Chittaranjan Das's claim to greatness lies more than anything else on his ardent patriotism. The Indian Posts and Telegraphs Department bought out a commemorative stamp on 5th November 1965, the occasion of his birth anniversary.
Date of Issue: 5.11.1965
Denomination: 0.15 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.63 x 2.62 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour:
Performation: 13 x 13
Paper: Printed on unwatermarked paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 2 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Electric Locomotive — Definitive Series


An early DC electric locomotive features in stamps of a definitive series issued in large numbers and used for many years. Another specimen of this series may be viewed at the album on railway stamps in the picture gallery in addition to the image above. To the right, a specially overprinted specimen is shown.
The production of electric locomotives commenced at Chittaranjan Locomotive works in 1961. The first 1500V DC WCM-5 Locomotive named 'Lokmanya' was commissioned by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru on the 14th of October 1961.
The stamp depicts a WCM-5 from Kalyan shed in its original livery.
Overprinted version
The International Control Commission consisting of representatives from India, Canada and Poland, was formed to supervise the agreement signed on July 21, 1954 between France and the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. The agreement provided for the temporary division of Vietnam at the seventeenth parallel until such time as elections could be held. Indian forces were stationed in Laos and Vietnam beginning in 1965 until 1968.The planned nation-wide elections never materialized. When the ICC was reconstituted as the International Commission for Control and Supervision in 1973, India opted not to participate.
The Indian Post and Telegraph department issued definitive series overprinted 'ICC' for use by the Indian contingent serving with the ICC in Vietnam
Date of issue: 1.7.1966 (normal); 2.10.1968 (overprinted for ICC)
Denomination: 10p
Thakkar Bappa

Thakkar Bappa was born on the 29th of November 1869 in a middle-class family of Bhanagar in Saurashtra. His father Vithal Das Thakur named the child Amrit Lal. He received his first schooling for benevolence and service to humanity from his father. He got his L.C.E (Licentiate in Civil Engineering) from Poona in 1890. He worked as an engineer creditably in Porbandar and later went out of India to serve in laying the first railway track in Uganda. He served also as chief engineer in Sangli state for some time. Here he saw the miserable conditions of scavengers who had to dispose the refuse of the whole town of Bombay. He was shocked to see the filthy colonies where the sweepers had to live and made a firm resolve to devote the rest of his life to alleviate the lot of these people. After this he resigned form service and in 1914 joined 'Servants of India' society. He was the inspiration for many missionaries in the cause of the service of the backward classes and the tribal people and for other constructive workers.
Date of Issue: 29.11.1969
Denomination: 20p
Signal Box Panel

The International Union of Railways, otherwise known as UIC was founded in 1922. Its objective is to standardize and improve on the railways with special regard to International traffic. The UIC is also responsible for ensuring co-ordination and unity of action amongst the International Railway Organization. Since 1950, the UIC has set-up 4 new offices, namely, (a) The office for Research and Experiments (ORE) for the pooling of means on technical research; (b) Information and Publicity Center of the European Railways (CIPCE) for publicity and public relations regarding the railway activities; (c) International Railway Documentation Bureau (B.D.C.) which facilitates exchange between the railways, (d) The Railway Films Bureau (B.F.C) which enables information to be exchanged in that field.
The Indian Railway has been associated with the International Union of Railways since 1957. The Union celebrated its golden jubilee in 1972. These celebrations had a special significance for India because on this occasion the UIC held a Colloquium on 'sharing of Railway Knowledge' which was presided over by the Chairman of the Indian Railway Board, and was attended by a number of representatives from railways of both developed and developing countries all over the world. Of all the members of the UIC, the Indian railways have the biggest route kilometrage. The Indian Posts and Telegraphs department bought out a commemorative stamp to mark the Golden Jubilee of the International Union of Railways. The stamp design is based on artwork by the well-known French artist George Mathieu.
Date of issue: 30.6.1972
Denomination: 20p
Lalit Narayan Mishra

Lalit Narayan Mishra was born in January 1923 at Basupatti in Saharsa district, Bihar. He took to politics in his student days, organized the Bihar Provincial Student Congress in 1941, and was its secretary in 1945-48. He did his MA in Economics from Patna university in 1948-48. His rise as a leader of national stature began in 1950 when he became a member of All India Congress Committee. He was a member of the first and second Lok Sabha. He was unanimously elected as a member of the Congress working committee in 1972. He held various high posts in government. He was Parliamentary secretary, ministry of Planning, labor and Employment (1957-60), Dy.Minister for Home affairs (1964-66), Dy.Finance Minister (1966-67), Minister of state for defence production (1967-70). From 1970 till Feb 4,1973 he was minister of foreign trade. On 5 Febrauary, 1973 he was appointed minister if railways with cabinet rank. As minister of railways, he visited Samastipur on 2 January, 1975 to declare open Samastipur-Muzaffarpur broad gauge railway line. A bomb explosion on the dais seriously injured him. He was rushed to the railway hospital at Danapur where he succumbed to his injuries on 3 January 1975.
Date of Issue: 3.1.1976
Denomination: 25 p, 50 p, Re.1, Rs.2
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.56 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Raw Sienna
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Unwatermarked adhesive stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 3 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Indian Locomotives


GIP No 1: This engine is representative of the earliest engines employed in India. To operate the train service between Bombay and Thane, the Great Indian Peninsular Railway ordered eight locomotives from Vulcan Foundry, England. These engines GIP Nos 1-8 were manufactured in 1852, bearing maker's numbers 324-331 and were, excepting two contractors locomotives of 1851, the earliest type in service on the railways of India. The first engine entered service in 1853.
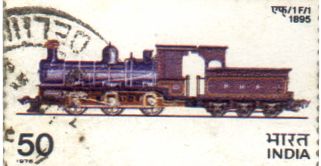
F/l - This was the most widely used engine on Indian Railways before Independence. It was extensively used on Rajputana Malwa Railway, which became the meter gauge section of the Bombay and Central Indian Railway. The first of these engines was built by Dubs & Company Glasgow in 1875. From 1895 these engines were also manufactured in India at the Ajmer Railway Workshop. These were withdrawn from active service in 1958. The engine depicted on the stamp was manufactured at Ajmer in 1895.
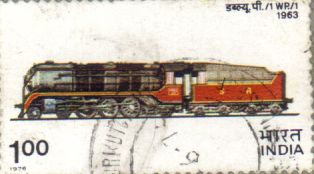
WP/I: The standard post-war broad-gauge express locomotive is the WP class 4-6-2 'Pacific' type. This design was the outcome of detailed study of previous types and incorporated the result of research into efficiency and mechanical details. Sixteen prototype engines were built in the United States in 1947 and after exhaustive trials and minor alterations, 300 further engines were ordered from a number of suppliers. In 1963, manufacture of this type was started at Chittaranjan Locomotive Works.
WDM2 Diesel: This is the most widely used diesel locomotive in India This locomotive is a mixed class design with 2,600 hp. weighing 113 tons and hauls freight trains of 2,250 tons and mail trains with 18 coaches. These engines haul nearly 56 per cent of the total freight traffic on the Indian Railways and important mail and express trains The Diesel Locomotive Works at Varanasi has a capacity to manufacture 120 such locomotives per year.
Date of Issue: 15.5.1976
Denomination: 25 p, 50 p, Re. 1, Rs. 2
Overall Size: 4.06 x 2.28 cms
Printing Size: 3.80 x 2.00 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 50
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 14 x 14.5
Paper: Printed on unwatermarked adhesive coated paper
Printing Process: Multicolor gravure process
Number Printed: 25p - 5 million, 50p - 3 million, Rs. 1 - 2 million, Rs. 2 - 2 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Foreign mail arriving in Bombay

The First Asian International Stamp Exhibition briefly called ASIANA-77 was held from October 19 to 23, 1977. The Philatelic Congress of India organized the exhibition, with the active participation and assistance of the Indian Posts and Telegraphs Department and also the Government of Karnataka. The exhibition was exclusively for the Asian and Australasian countries and under the patronage of the Inter-Asia Philatelic Federation (FIAP) which is the Asian chapter of the Federation Internationale de Philatelic (FIP). Representatives from 7 European countries to safeguard the interests of stamp collectors at international level founded FIP in 1926. At present, there is hardly any National Philatelic Federation of a country, which is not affiliated, with the FIP. The FIP has set up standards rules for holding the International Exhibitions under their patronage. The FIP has categorized harmful, improper and undesirable stamp issues, which they have banned for exhibiting in any of the International Exhibitions under their patronage.
FIAP was organized in 1975 to strengthen the Philatelic activities among Asian and Australasian countries. To increase the participation of Asian countries in International Exhibition, the idea of Regional Exhibitions was mooted. ASIANA-77 was a landmark in the philatelic history of India as not only the country had the honor to hold the First Asian International Stamp Exhibition but also some of the rarest stamps were on display in this exhibition for the first time in India. The Indian Posts and Telegraphs Department bought out two special postage stamps on the occasion of the First Asian International Stamp Exhibition - ASIANA-77. The stamp in Re.1 denomination depicts a pair of a famed Red Scinde Dawks of 1852 (the first Stamp in Asia). The stamp in Rs. 3/- denomination shows foreign mail arriving at the Ballard Pier in Bombay in 1927. It was adapted from a photograph appearing in the Annual Report of Indian Posts & Telegraphs Department for the year 1926-27.
Date of Issue: 19.10.1977
Denomination: 100 p, 300 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Unwatermarked adhesive stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 2 million each
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Centenary of Darjeeling Himalayan Railway

The snow peaks of the magnificent Himalayas have since time immemorial enchanted saints, pilgrims and tourists for various reasons. Railways, in their own way, have tried to 'ascend' the hills. The eternal Darjeeling-Himalayan Railway line having a two feet wide track, conceived by Franklin Prestage, the agent of the Eastern Bengal Railway, links Darjeeling to Siliguri, a distance of 87.48 Kms. A unique engineering feat passing through different climate zones offers a picturesque and science beauty. Laid on the famous Hill Cart Road, the Railway line appears to be playing hide seek with the road as they criss-cross each other at several places. The line between Sukna and Darjeeling is almost all along located on the road-bench, either skirting hillside or on the far edge of the road. The alignment passes through hills and gradually climbs up to the maximum altitude of 2,258 meters at Ghum. The honor of blazing the trail of the first railway train across the Alps, the first experiment for construction a hill railway, goes to Chega, an Austrian. He was the first to apply the principle of artificially lengthening the line by looping in order to flatten the gradient. The engineers of Indian Railways successfully applied the principle in constructing Darjeeling-Himalayan line thereby completely obviating the necessity of expensive tunnels. Another method adopted on the route is reversing a zigzag movement, each leg of this move being utilized to gain additional height, although this means the train moving backward on the central leg. The need for tunnels was completely obviated by means of 'loops' and 'reverses'. There are 4 loops of which the most renowned one is the Bastasia loop, 5 reverses in the shape of 'Z', 5 major and 498 minor bridges and 177 unmanned level crossings on the section. Around 90% of the length of track is on curves, the sharpest curve having a radius of 59 feet and steepest gradient of 1 in 22. The construction of the section began in 1878 and could be completed only in July, 1881. The Government of India purchased it in October 1948 with a view to fit it in the system of New Assam Link Project. This narrow gauge line was extended from Siliguri to New Jalpaiguri in 1962.
The stamp features 0-4-0 T Darjeeling Himalayan loco and passenger cars.
Date of Issue: 18.12.1982
Denomination: 285 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Unwatermarked adhesive stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 20,22,000
Designers/Printers: Indian Security Press
Inpex-82

Since Independence, Indian Posts & Telegraphs Department has made pioneering efforts in promoting philately through exhibitions. To celebrate the centenary of Indian postage stamp, the first International Stamp Exhibition was held in New Delhi in 1954. The first national exhibition was held in 1970 in New Delhi, the second in Calcutta (1975) and the third one at Banglore (1977). An International exhibition, INDIPEX 73 was held in New Delhi in 1973. The first international exhibition under the aegis of the Federation Internationale de Philatelie was INDIA 80, held in New Delhi in 1980. The first and perhaps the only all Asia exhibition, ASIANA 77 was held in 1977 in Banglore. Besides these national and international exhibitions, the Postmasters General have been organizing exhibitions from time to time at the state, region and district levels all over the country. The Fourth India National Exhibition, INPEX-82 was held in New Delhi from 30th December 1982 to 5th January 1983 by the P & T Department, in co-operation with the Philatelic Congress of India. To mark the occasion, Indian Posts & Telegraphs Department issued a set of two stamps.
The 50 P. denomination stamp, designed by C.R. Pakarashi, shows a vintage four-wheel composite rail coach comprising Railway Mail Service Van in the middle with passenger sections on either side. An early steam engine of Indian Railway is shown in silhouette.
Date of Issue: 30.12.1982
Denomination: 50 p, 200 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms, 4.83 x 3.66 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms, 4.48 x 3.31 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35,20
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x13, 14 x 14
Paper: Unwatermarked adhesive stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 2 million each
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Centenary of South Eastern railway




The South Eastern Railway had its beginning 100 years ago when its predecessor, the Bengal-Railway Co., a company formed in London, signed a contract with the Secretary of State in Council in India to take over the meter gauge Nandgaon Nagpur line on 9th March, 1887. Subsequently, the Kanti-Umaria line, now in the then Central Province, was taken over by this Railway and the Nagpur-Chattisgarh Railway converted to broad gauge. In the next ten years, this railway came up to Calcutta, which was then declared as its headquarters and also up to the coalfields of Bengal -Bihar with a line connecting Asansol in the then East India Railway. The Bengal-Nagpur Railway was brought under direct State management on October 1, 1944 on the expiry of all contracts between the companies and the Government. After Independence, the Bengal-Nagpur Railway was merged with the then East Indian Railway and one zonal railway unit was founded with headquarters at Calcutta. This was found to be unwieldy and on 17th June 1955, the then Railway Minister, Sri Lal Bahdur Shastri announced the separation of old East Indian Railway and Bengal-Nagpur Railway as two separate zones with headquarters of both in Calcutta. The old Bengal-Nagpur Railway sections constituted the South Eastern Railway. SER connects Calcutta with Bombay and Madras. This Railway extends up to Nagpur on the Bombay route, a distance of 1132 kms, and Waltair on the east section to Madras, a distance of 879 kms.
The 150p stamp depicts an early meter gauge steam engine 0-6-4T, No. 691.
The 400p stamp features the early broad gauge 2-8-2 steam engine of 1890.
The 100p stamp depicts the emblem of SER.
The 200p stamp depicts an electric engine and passenger cars on a viaduct
Date of Issue: 28.3.1987
Denomination: 100 p, 150 p, 200 p, 400p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Imported unwatermarked adhesive gravure coated stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 1.5 million each
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
100 years of Victoria Terminus, Bombay

The Great Indian Peninsula Railway constructed the administrative headquarters of the Central Railway known as Victoria Terminus Station building in 1888. The chief engineer of the Railway was Mr. Wilsom Bell Mice, and the building was constructed under the guidance of Mr. F.W. Stevens, consulting architect. The building, which took 10 years to complete, is in late Italian Medieval Gothic style, and was named Victoria Terminus in celebration of Queen's Golden Jubilee on June 20, 1887. Well-proportioned, ornamental arches and spires and domes, give it the dignity of a cathedral. The crowning point of the whole building is the central dome carrying at its apex, a colossal 16'6" high figure of a lady pointing a flaming torch upwards in her right-hand, and a spooked wheel low in the left-hand, symbolizing 'Progress'. This dome has been reported to be the first octagonal ribbed masonry dome that was adapted to an Italian Gothic style building. The construction of the interior of the dome is entirely open, and exposed to view from the ground floor, and the dome-well which carries the main staircase, has been artistically decorated. On the facade are also large bass-relief of 10 Directors of the old Great Indian Peninsula Railway Company two of whom were Sir Jamsedji Jijibhoy and Sir Jagannath Shankarseth.
Old records show that most of the bass-relief and some of the statuary was executed by Indian Craftsmen, and students of the Bombay School of Arts, from models supplied and designed by an Indian teacher. Only the statues denoting 'Progress', 'Engineering & Science', 'Shipping & Commerce' and 'Agriculture' were sculptured in England out of Indian Porbunder sandstone. The entrance gates to Victoria Terminus carry two main gate columns, which are crowned, one with a Lion (representing the United Kingdom) and the other with a Tiger (representing India), both sculptured in Porbunder sandstone. Victoria Terminus Station building has been considered one of the finest stations building of he world, and architecturally one of the most splendid and magnificent late Italian Medieval Gothic edifices existing. In 1969 the statue of Progress was damaged due to lightning, but the Central Railway authorities with the help of Prof. V.V. Manjrekar of J.J. School of Arts successfully restored it.
Date of Issue: 30.5.1988
Denomination: 100 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Three colour
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Indigenous unwatermarked PG matt coated stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 1.5 million each
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
India 89 World Philatelic Exhibition, Early RMS cancellation


As a prelude to India-89, World Philatelic Exhibition, the Department of Posts issued a series of stamps. The fourth set issued, carries two cancellations, one of the RMS (Railway Mail Service) and the other of the DLO (Dead Letter Office). The Indian Postal System is one of the largest in the world. In the nineteenth century, the geographical area covered by the system was very much larger. It included undivided India and Burma and also certain out-post of the British Empire like Aden, Singapore and Shangai where Indian Stamps were used. This, along with the multifarious activities undertaken by the system itself, made a study of the Indian postal history interesting as well as instructive for a philatelist specializing in postal history collections. Postal history is the study of routes, rates and markings. The markings are by far the most colorful aspect of such collections. It was, therefore, appropriate that postal cancellations were chosen as the subject for these set of stamps.
The first stamp depicts one of the earliest hand stamps of the traveling post office in the 'Allahabad-Cawnpore' railway sector and this postmark was in use from December 1864 to 1869. The traveling sorting offices between these two places used it. The first Traveling Post Office was established on 1st May 1864 under a Superintendent at Allahabad. The TPO operated on the 'Allahabad-Crownpore' and 'Calcutta-Delhi' railway sector. The circular postmark shown on the stamp has a diameter of 25 to 26 ms with 'TRAVELLING' along the upper rim of the circumference and 'POST OFFICE' along the lower rim, with No. 1 of the set, date and 'AC' in three horizontal lines in the space within the circle. This cancellation was used by the 1st set of the experimental TPO on 21st August 1864. The second stamp depicts the type of cancellation used by the Dead Letter Offices in 1886.
Date of Issue: 20.12.1988
Denomination: 200 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 6 sheetlet
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Imported unwatermarked adhesive gravure coated stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 1.5 million each
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
J.S Sett & C.R Headquarters

Jagannath Sunkersett was born on February 10, 1803, in a wealthy Murkute family of Daivadnya community. His father was a rich businessman and a landlord. Jagannath received his early education from private tutors and soon became fluent in Marathi, Gujarathi, Sanskrit and English. He wanted to see an all round development of Bombay. His initiative in this direction saw the setting up of the J.J.School of Art, The Prince Albert Museum and the Victoria Gardens. He was also instrumental in founding the Royal Asiatic Society. Visualizing the importance and requirement of faster means of bulk transportation in the future, Jagannath Sunkersett formed the first Bombay Steam Navigation Company. He also realized the need for the Railways. He formed the first Inland Railway Association, which persuaded the British to lay tracks from Bombay's Victoria Terminus to Thane. This later came to be known as the G.I.P. Railway. He was made one of its first Indian Directors. The stamp depicts Jagnnath Sunkershett along with the Headquarters of Central Railways symbolizing his efforts in the establishment of the first railway line in Bombay.
Date of Issue: 15.02.1991
Denomination: 60 p, 650 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Two color
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Indigenous unwatermarked adhesive gravure coated stamp paper
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 6 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Mountain Locomotives




Neral - Matheran Railway Line (100P) the line was constructed in 1907. The gauge of line is 2 ft. The train was hauled earlier by 0-6-OT tank type locomotive built by Orestein and Koppel of Berlin. The stamp depicts 0-6-0 T ML 1905 steam loco
Kalka-Shimla Line (1100P): It was opened to traffic in 1903. The gauge of the track is 2'6". This section has 102 tunnels on 96 km run and ascends from 643m at Kalka to 2042m at Shimla. The steam locomotives were (2-6-4T) tank type built between 1904 to 1935 in Britain (Class K-1, K-2 and K.C. with Walsharet valve gear) and Germany (Class ZF, ZF-1 with caprotti poppet valve. The stamp depicts 2-6-4 T ZF 1934 steam loco
Darjeeling-Himalayan Railway (600P): This two feet wide track, conceived by Franklin Prestage, the agent of the Eastern Bengal Railway, links Darjeeling to Siliguri, a distance of 87.48 Kms. The alignment passes through hills and gradually climbs up to the maximum altitude of 2,258 meters at Ghum. Around 90% of the length of track is on curves, the sharpest curve having a radius of 59 feet and steepest gradient of 1 in 22. The stamp depicts 0-4-0 T B 1889 steam loco
Nilgiri Hill Railway (800P): Starting from Mettupalayam to reach Ooty, the train takes 4 hours to cover a distance of 52 km. It was constructed between 1885,and 1908. Bayer and Peacock Co. of Manchester manufactured the earlier locomotives. They had a rack and pinion system of holding them on steep gradient. Later Rack and Adhesion 0-8-2(T) types of steam locomotives were supplied by Swiss Locomotive Works between 1940 and 1952. The stamp depicts 0-8-2 T X 1914 steam loco
Date of Issue: 16.4.1993
Denomination: 100 p, 600 p, 800 p, 1100 p
Overall Size: 3.91 x 2.90 cms
Printing Size: 3.55 x 2.54 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 35
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Imported unwatermarked gravure coated gummed stamp paper in sheets 50.8 x 53.5 cms
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 1 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
Silver Jubilee National Rail Museum

Indian Railways set up the National Rail Museum in 1971. The Museum displays, both in the indoor gallery and the open yard, a good sampling of the history of Indian Railways. It provides an excellent opportunity to research students, railway enthusiasts, philatelists and educational establishments to cover the whole era at one place. In connection with the Silver Jubilee of National Rail Museum a commemorative stamp of 500P was issued on 7 October 1996.
The stamp depicts the 145-year-old steam locomotive the 'Fairy Queen' and another steam locomotive Ramgotty built in 1862.
Date of Issue: 7.10.1996
Denomination: 500 p
Overall Size: 4.05 x 4.85 cms
Printing Size: 3.65 x 4.40 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 40
Colour: Four color
Perforation: 13.5 x13.5
Paper: Matt chromo
Printing Process: Photo offset
Number Printed: 1 million
Designers/Printers: Calcutta Security Printer Ltd.
Konkan Railway

It was in 1882 that the first plans were made to link the picturesque western coast of India with a railway line. But the formidable Sahyadri mountains, the innumerable creeks and rivers proved too great a challenge at that time. The Railway System had begun just a few decades earlier. The first railway line on the Indian sub-continent, from Bori Bunder to Thane-a distance of 21 miles had been opened to traffic on April 16, 1853. Since then, it had grown to a total of 62,915 route kilometers. However on the western coastline of the country, there was a crucial missing link. In 1984 more than century after the first tentative survey, fresh plans were drawn up for a railway along this route. The survey was conduct over four years, up to 1988 and the Konkan Railway Corporation Ltd. (A Government of India Undertaking) was set up with Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka and Kerala in 1990 under the Build Operate and Transfer (BOT) principle. It was a formidable task. The terrain through which the line transverse is the most difficult encountered in the history of railway construction. Crossing the route involved building 92 tunnels, 172 bridges,2819 minor bridges and 59 stations. Some tall viaducts were also needed to be built, such as the one on the Panval Nadi valley in Ratnagiri, the tallest bridge in Asia. The construction was finally completed on January 26,1998 in the golden jubilee year of Indian independence.
Date of Issue: 1.5.1998
Denomination: 800 p
Overall Size: 3.50 x 7 cms
Printing Size: 3.50 x 7 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 12
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Imported unwatermarked adhesive gravure coated stamp paper in sheets 50.8 x 53.5 cms
Printing Process: Photogravure
Number Printed: 0.7 million
Designers/Printers: India Security Press
A. B. Walawalkar

Born on December 27,1897, and hailing from village Walawal in Kudal Tahsil of Sindhudurg District in Maharashtra , Shri Arjun Balwant Walawalkar joined Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway (presently Western Railway) in its Drawing Department in 1922. He was the visionary who dreamt and conceived Konkan Railway Project and his detailed proposal was ready as far back as 1952 when he published a booklet entitled 'Konkan Railway Project'.
While formulating the scheme, Shri Walawalkar undertook intensive and extensive tours in the Konkan Region and worked ceaselessly and tirelessly in propagating the scheme and enlisting popular support for it. He wrote a number of articles in the newspapers, organised conferences, seminars and exhibitions, called on the successive Railway Ministers and Chief Ministers of the concerned States. Even public ridicules and criticisms did not deter him from his dream project.
On December 23,1970, Shri Walawalkar breathed his last but not before bringing his dream project within the realm of realization. Now his dream has come true as a broad gauge superfast link between Mumbai and Mangalore- Konkan Railway is the biggest new railway line construction undertaken on the Indian sub-continent in the present century. This 760km-long broad gauge line passes through the most difficult terrains and involves 180 major bridges, over 1600 minor bridges and tunneling for a total length of 84 kms. The project took a little over seven years and was commissioned on January 26, 1998 The Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications, released a commemorative postage stamp in honour of late Shri Arjun Balwant Walawalkar, who has been described as 'father of the Konkan Railway Project'.
Date of issue: 9.10.1999
Western Railway: Churchgate Building, Mumbai

Churchgate building was originally the headquarters of Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railways (BB&CI), one amongst the famous railway companies in British India. BB&CI was incorporated in 1855 to start a railway route from Surat to Bombay to ensure regular supply of cotton in Gujarat area. The headquarters was originally located at Surat and later shifted to Mumbai Construction of the headquarters buildings at Churchgate was started in 1894 and completed in 1899 under the direction of Mr. Fedrick William Stevens. The construction cost then was Rs. 750,000.
The tower of this building is square from the base up to 100 feet when it becomes octagonal and is surmounted by a circular dome. The building was an oriental character with facings of rough-hewn basalt inlaid with bands of Bassien sandstone and white stone dressings. The dome looks like a Gothic Revival composition, as that is the structural language employed.
Date of Issue: 27.12.1999
Denomination: 1500p
100 years of Railways in Doon Valley

In the later half of nineteenth century, despite laying of railway line up to Hardwar and Saharanpur, access to the valley and the nearby Mussoorie hill station was extremely difficult on account of the steep Shivaliks skirting the valley from south east to north west. The tourists traveled up to Saharanpur by rail and used bullock or horse driven carts for Dehradun or up to Rajpur from where pones or dandies carried them to Mussoorie. Railway line between Hardwar and Dehradun was sanctioned on 18th November 1896. The contract for the construction and working of Hardwar-Dehra Railway between the Secretary of State and the Hardwar-Dehra Railway Company was signed on 26th March 1897. Land was made available free by the government. Work on the track and buildings was completed by early 1900 at a cost of about Rs.26 lakhs and the line was opened for traffic on 1st March 1900. Opening of railway led to prosperity of Dehradun. Mussoorie and its adjoining areas also gained substantially from the far easier access.
Date of Issue: 6.5.2000
Denomination: 1500 p
Overall Size: 4.05 x 4.80 cms
Printing Size: 3.60 x 4.40 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 40
Colour: Multicolor
Perforation: 13.5 x 13.5
Paper: Matt Chromo
Printing Process: Photo Offset
Number Printed: 0.7 million
Designers/Printers: Calcutta Security Printers Ltd.
150 Years of Railways in India

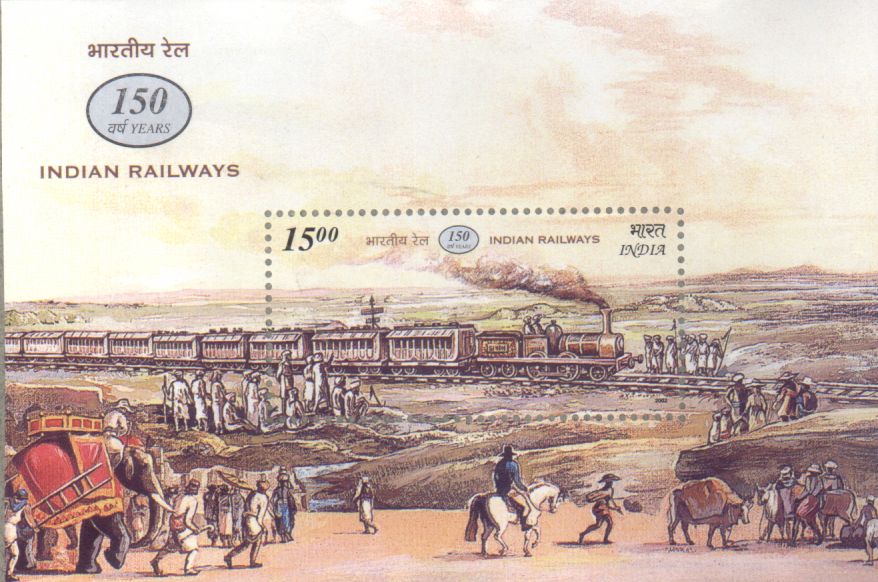
Railway have been a great integrating force in India for more than a century, particularly so after the attaining of independence in 1947. It has bound the economic life of the country and helped in accelerating the development of industry and helped in accelerating the development of industry and agriculture. It has brought together people from the farthest corners of the country and made possible the conduct of business, education, pilgrimage and tourism. The history of Railway in India began on 16th April 1853, when the first train steamed off from Boribunder to Thane, covering a distance of 34 Kilometers. From such a modest beginning, the Indian Railways have grown into a large network of about 7,000 stations spread over a route length of nearly 63,000 Kms. Today it is one of the largest organizations in the world, employing the work force of 16 lakhs. It provides the principal mode of transport for freight and passengers in India. The country observed an year long celebration in 2002-03 to mark the 150 anniversary of India's first train journey. The Depts. posts tried to capture the spirit of the vent with issue of commemorative stamp and the first miniature sheet in Indian railways. The design of the stamp and the miniature sheet tries to re-create the Indian landscape of 1853, with the first train chugging away in the distance, on its journey to Thane on the 16th of April.
Date of Issue: 16.4.2002
Denomination: 1500 p
Overall Size: 5.25 x 2.62 cms
Printing Size: 5.25 x 2.62 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 27
Colour: Six color
Perforation: 13.5 x 13.5
Paper: Matt Chromo
Printing Process: Photo Offset
Number Printed: 3 million
Designers/Printers: Calcutta Security Printers Ltd.
100 years of Kalka Shimla railway

The journey from Kalka to Shimla is absolutely out of this world. The toy train provides a breath-taking view of the Kushalya river, the moment it enters the foothills. On 9th November 1903, a 96 km. railway line was launched in the limestone and shale rocks of the Shivalik Hills after three years of dedicated labour. Laid on sharp curves, the line passes over 864 bridges and through 102 tunnels using a narrow gauge of two feet and six inches in deference to hill formation and gradient.
Nature unrolls its bounty as one travels. Gurgling brooks flowing down mountains, passing under the stone bridges; greenery and fragrances that live beyond photographs; clouds of mist gingerly touch the traveler. The train meanders through Kumarchatti, and then enters the Barog tunnel (1144 mts. Long) which crosses the Punchmunda ridge about 900 feet below the road. At Barog, it is mealtime on the morning trip. Though the English firm of 'Spencers' which built the restaurant at Barog is no longer there, the hospitality continues to live.
From Barog to Kandaghat, the train runs downhill, past beautiful and quaint retreats of Solan and Saloghra. At Shogi, a heartwarming view of the Chail Valley brings numerous anecdotes associated with a Prince from Punjab. Banished from English society at Shimla, he built for himself a palace at Chail, a nearby resort. Past Taradevi, the railway takes one under Prospect Hill to Jutogh, winding its way like a naughty current of air teasing, till it pauses at Summer Hill. Finally, under the Inverarm Hill, one emerges like a happy child at Shimla.
Date of Issue: 9.11.2003
Denomination: 500 p
Overall Size: 2.9 x 3.91 cms
Printing Size: 2.9 x 3.91 cms
Number per Issue Sheet: 50
Colour: Four color
Perforation: 13 x 13
Paper: Imported unwatermark stamp paper
Printing Process: Photo Offset
Number Printed: 3 million
Designers/Printers: Eagle Press Pvt.Ltd.
Kalia Bhomora Bridge

The River Brahmaputra has remained a technical challenge for decades due to its ferocity and magnitude along with most unpredictable behavior. The first ever bridge across the Brahmaputra was constructed by the Indian Railways in 1962 at Saraighat near Guwahati. Incidentally, Indian Railways on behalf of the North Eastern Council also constructed the second bridge. The bridge forms a part of the total schemes of providing a 23km-long link between National Highway #52 on the north bank and National Highway #37 on the south bank. The need for a second bridge across the Brahmaputra on its course of 920km in India was long felt from socio-economic considerations of the North Eastern States, which remained connected with the rest of the country only through the existing bridge at Saraighat. The North Eastern Council - an agency under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Govt. of India, sponsored the project in November 1975. After detailed studies, the project was finally commissioned in March 1979 by awarding the prestigious construction of the 3km-long bridge alongside a massive guide bund of 2km including a 1.7km river approach for Indian Railways - in recognition of the technical excellence of Railways in bridging all the major rivers of the country. The NE Railways Construction Organization took up this challenging task and physical work on the bridge started in October 1981. The bridge was completed in a record time of 64 months by working against all odds.
KALIA BHOMORA after whom the bridge has been named was a prominent figure of the 18th century in the history of Assam. He was appointed as autonomous Governor, called Bar Phukan in Guwahati. He fought several battles to crush rebellions against the Ahom Kings. He organized and trained armies to a high level of war skill. Apart from being an efficient General and an able administrator he made outstanding contribution to religion and public welfare. He had conceived a plan to build a bridge across the river Brahmaputra at Bhomoraguri, near Tezpur. He made advanced preparations for the actual construction of the bridge. Even today large sal wood logs and other material for the construction of the bridge can be found in this area. The site of the modern bridge inauguration was the same as that chosen by Kalia Bhomora.
The 200p multicolor stamp shows an over view of the Kalia Bhomora Bridge across the Brahmaputra river in Tezpur.
Date of Issue: 14.4.1987
Denomination: 200 p
Kirloskar Centenary

The Kirloskar story began in 1888 when Laxmanrao Kirloskar set up a small bicycle repair shop at Belgaum. Laxanrao and his brothers set up a model industrial colony called 'Kirloskravadi'. Their new company 'Kirloskar Brothers Limited' was the parent of all the 26 companies that flourish under the Kirloskar banner today. The end of World War II brought a tremendous upsurge of industrial activity under Laxmanrao's eldest son 'S.L.'. Kirloskar Electric Company Limited at Bangalore, and Kirloskar Oil Engines Limited at Pune were established in 1946, the latter was in collaboration with U.K based Associated British Oil Engines Export Ltd., the first instance of an Indo-Foreign collaboration. Next came Kirloskar Pneumatic Company Limited (1958) and Kirloskar Cummins Limited (1962) both at Pune. The latter won a citation from Lloyd's Register of Shipping. Later the Kirloskar diversified into industrial consultancy and five star hotels among other activities. Today the Group's annual sales exceed Rs. 700 crores. It has been a long march from a small shed to 26 powerful units, from a work force of four to over 20,000 employees- the Kirloskars have kept pace with India's march to freedom, to self-sufficiency, to export around the globe, and contributing to the country's core industries such as defence, power generation, oil and gas, agriculture, steel, coal and mining, railways and transportation. The Kirloskars describe themselves as 'businessmen engaged in winning freedom and prosperity for our country through our chosen method - engineering excellence'.
Date of Issue: 20.6.1989
Denomination: 100 p
Sayaji Rao Gaekwad III

Sayaji Rao Gaekwad III (1863-1939) was born on 11th march, 1863, in a village in the Nashik District of the then Bombay Presidency. Originally named Gopalrao, he, with his two brothers, went to a dilapidated primary school, the only one in the village. At the age of 13, the Dowager Maharani of Baroda State adopted him. He was re-named Sayaji Rao Gaekwad III and put through a crash program to prepare him for his life as a ruler. Almost from the word go, Sayajirao was in conflict with the British, having continuous and longstanding verbal and written disputes with the British Residents. On assuming the reins of Government, some of his first tasks included education of his subjects, upliftment of the downtrodden, judicial, agricultural and social reforms, building a network of railways to connect areas of his dispersed territories. His educational and social reforms included, along others, ban on child marriage, legislation of divorce, removal of untouchability, spread of education development of Sanskrit and ideological studies, religious education, encouragement of fine arts and his total commitment to free and compulsory primary education, which placed his territory far in advance of contemporary British India. Fully aware of the fact that he was a Maratha ruler of Gujarat, he identified himself with the people and developed their cosmopolitan attitude and progressive, reformist zeal. His rich library became the nucleus of today's Central Library of Baroda. He was the first Indian Ruler to introduce, in 1906, compulsory and free primary education in his State. Though a prince of a native state, an admirer of the English people and in many respects of the English rule in India, he jealously guarded his rights and status even at the cost of annoyance to the Indian Government. The English bureaucracy considered him a 'Patron of Sedition' as he talked to his countrymen on love of the country, Swadeshi, Indian heritage and the need for political reforms. After a long and eventful rule of 63 years, Sayajirao Gaekwad III died on 6th February 1939.
Date of Issue: 6.10.1989
Denomination: 60 p
Madhavrao Scindia

Madhavrao Scindia, the only son of Jiwajirao and Vijayaraje Scindia, was born on March 10, 1945. He did his higher studies in the United Kingdom, before entering the public life at the age of 25. He rose to serve in the Union Council of Ministers and held various important portfolios. As Minister of Railways, turning it to be a 'golden era', he introduced superfast short distance passenger trains like the Shatabdi Express and also undertook great efforts to computerize rail reservations and booking. As Minister of Civil Aviation and Tourism, he opened up the Indian skies for the private airlines and provided new destinations for the Indian tourists. In his brief tenure as the Minister of Human Resource Development, he outlined bold proposals to increase budget allocations for primary education and to set up the National Cultural Fund. He was deeply committed to the cause of education, more particularly the education of girls.
Madhavrao Scindia also served as the Deputy Leader of Opposition in Parliament. He excelled in all the fields where he remained and left shining examples for others to follow. He had been the Chairman of the Committee on Science and Technology during 1990-91. His special area of interest, apart from education, was wildlife preservation and development of sports, cricket and golf in particular. He was the President of the Board of Control for Cricket in India during 1990-93. The country lost a great aspiring leader, to untimely death in a plane crash near Kanpur, at the age of 56 years.
Date of Issue: 10.3.2005
Denomination: 500 p
